How to use efficiently Postman
TL;DR
Postman is a great tool for testing REST API. It is very convenient to use it for testing WebStore API. However, it is not very convenient to copy/paste JWT token every time you need to test a new request due to the token expiration, server restart, etc. This article describes how to automate this process.
Environment variables
Define first environment variables for your Postman collection. You can do it in the following way:
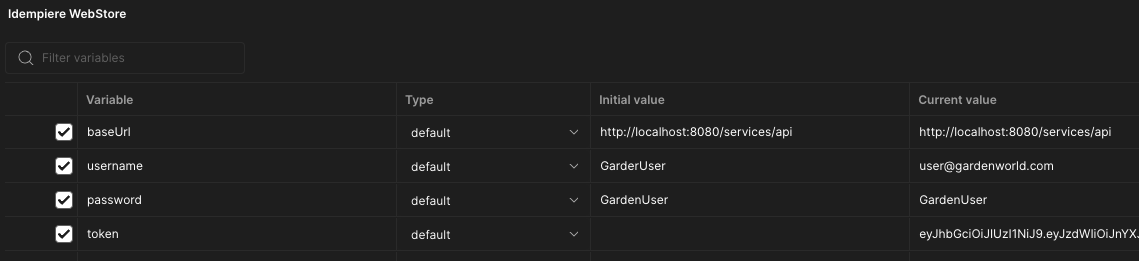
Note: No need to define token variable. It will be defined automatically.
Pre-request script
Add the following script to the pre-request script section of your Postman collection:
pm.sendRequest(
{
url: pm.environment.get("baseUrl")+"/auth/login",
method: 'POST',
header: 'Content-Type: application/json',
body: {
mode: 'raw',
raw: JSON.stringify({
"username": pm.environment.get("username"),
"password": pm.environment.get("password")
})
}
}, function (err, response) {
pm.environment.set("token", response.json().token);
});
What does this script do?
- It sends a request to the login endpoint with the username and password from the environment variables.
- It saves the JWT token from the response to the environment variable
token. - This variable will be used in the Authorization header for all requests in the collection.
Note:
- Don’t forget to add the
Authorizationheader to the collection.- Type:
Bearer Tokenfrom context menu. - Token:
{ {token} }from the environment variable.
- Type:
- This exemple uses the
baseUrl,usernameandpasswordenvironment variables. Login endpoint from webstore-api is/auth/login. You can change it to your own.values.
Conclusion
Now you can test your API without manual copy/paste of the JWT token. Use Inherit auth from parent for all requests. It will be executed automatically before each request. Nice and easy!